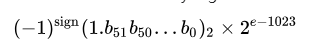引言
RISC-V(下简称RV),作为一种开源的CPU架构,其灵活的指令集和可扩展性为开发者提供了丰富的设计选项。在数值计算中,浮点数的处理尤为重要,而浮点数舍入(rounding)机制则是确保计算精确性和效率的关键一环。本文将聚焦于RV64架构下浮点数的舍入(浮点到浮点)在Go语言中实现,特别是通过FCVTDL/FCVTLD指令的应用来探讨实现的原理。
想看代码的朋友,可以直接看我提交到Go官方的代码参考
golang/go/commit 90391c2
啥是舍入(rounding)
Round(2.5) = 2,就是一种舍入方法(四舍五入嘛)
实际编码中的问题
第一个问题是,既然RV64有浮点转换指令,那直接用不就行了么?
事情并没这么简单,由于RV64并不像其他架构有单独的浮点到浮点的取整指令(例如arm64的FRINTMD),因此只能用FCVT (floating point convert)先转换到整数寄存器中,再从整数寄存器中转回浮点寄存器。
例如浮点值X,在寄存器FA0中,需要以下指令(注:Go的Asm,从左到右):
FCVTLD FA0, A0
FCVTDL A0, FA0
坑就在此出现了!
IEEE 754 中 -Inf (负无穷大)的二进制表达是0x7fffffffffffffff,而根据RV64指令集手册,对于不合格的浮点输入,就“凑到相近的值”并复制到整数寄存器中了。
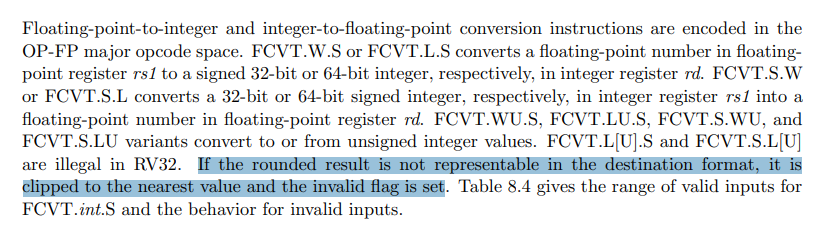
Floor(-Inf) -> int64(0x7fffffffffffffff)
这下热闹了,整数0x7ff...ff是合法的整数。当你转回浮点时……就变成了float64(9.22e+18)。这意味着
非法数值变成了合法数值
例如这个issue:https://github.com/golang/go/issues/68322
那么通过RV64的FCLASS (浮点类型)指令提前判断呢?可以是可以,但由于多重判断是否数值在取整范围内,经过测试速度不够快(性能下降60%),并不符合我们程序员对于“高效”的追求。如果要达成快捷的判断非法输入的方法,需要我们回顾一下IEEE 754的表达方式。
RV64中浮点数的表示
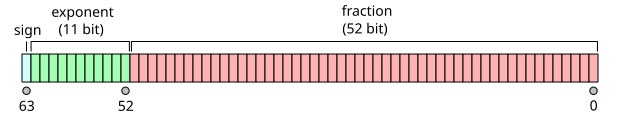
在RV64浮点数中的表示遵循IEEE 754标准,该标准定义了浮点数的符号位、指数和尾数部分。
IEEE 754标准定义了浮点数在计算机中的存储方式,主要包括三个部分:符号位(S)、指数(E)和尾数(M,也称为有效数字或小数部分)。对于双精度浮点数(即double类型,在大多数现代计算机中占用64位),其格式如下:
- 符号位(1位):位于最高位,0表示正数,1表示负数。
- 指数(11位):用于表示浮点数的指数部分,采用偏移量编码方式(对于双精度,偏移量为1023)。
- 尾数(52位):表示浮点数的有效数字部分,但隐式包含了一个前导的1(除了表示0或次正规数的情况)。
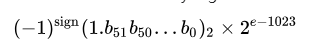
例如要表达IEEE754 DP 0.375,可以拆解为:0.25*1.5
- 正数,符号位为0
- 指数需要0.25,2-2,通过补码,即0x3FD
- 尾数1.5,则是1+2-1,即0x8(1000_0000)b
二进制即0x3FD8_0000_0000_0000
其中IEEE 754 DP非法的输入分别是:
- ±Inf(正负无穷大)
0x7FF0_0000_0000_0000
- NaN(Not a Number,压根不是个数)
NaN也有很多中表达方式,有
- qNaN
0x7FF8_0000_0000_0001
- sNaN
0x7FF0_0000_0000_0001
- 特殊NaN
0x7FFF_FFFF_FFFF_FFFF
如果仔细留意的话,你会发现,所有的非法输入都是通过指数位表示的,而且都相当大(0x7FF= 2047d - 1023,实际为1024),那么,我们只需要通过右移52位,并加以掩码(mask)去除正负影响,就可以判断一个浮点数是不是非法输入(0x7FF)。重点来了
这个方法可以顺便判断是不是整数取整范围
因为浮点数能取整,就意味着指数小于53,即整个数小于253,如果对大于这个数取整就会出现未定义行为了,所以Go语言限制,必须在这个范围内,超过的合法输入原样输出即可。
var x float64
maskedExp := (math.Float64bits(x) >> 52) & 0x7FF
if maskedExp > 1023 + 52 {
return x
}
// FCVTLD x, A0
// FCVTDL A0, x
这样是不是就好了?不……还有一个坑……
±0没办法处理
所以最后需要使用RV64的FSGNJD指令,将x中的符号位拷贝复制过来。
最终效果
见前面提到的golang/go/commit 90391c2,提升300%
│ math.old.bench │ math.new.bench │
│ sec/op │ sec/op vs base │
Ceil 54.09n ± 0% 18.72n ± 0% -65.39% (p=0.000 n=10)
Floor 40.72n ± 0% 18.72n ± 0% -54.03% (p=0.000 n=10)
Trunc 38.72n ± 0% 18.72n ± 0% -51.65% (p=0.000 n=10)
geomean 33.56n 20.09n -40.13%